.

STS-30
Space Shuttle: Atlantis
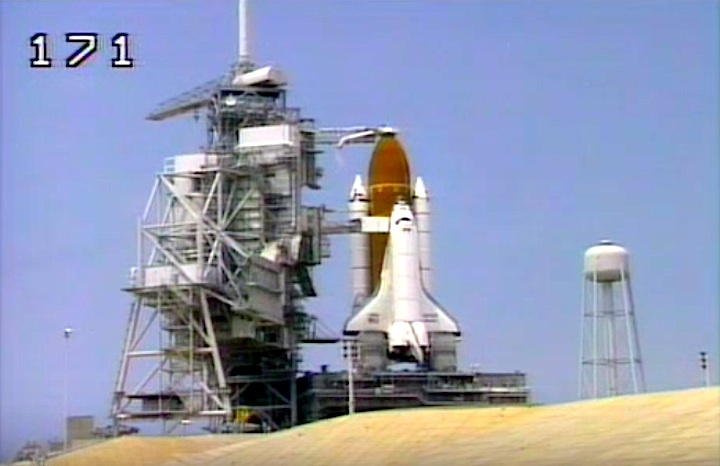
Launch Pad: 39B
Launch Weight: 261,118 pounds
Launched: May 4, 1989, 2:46:59 p.m. EDT
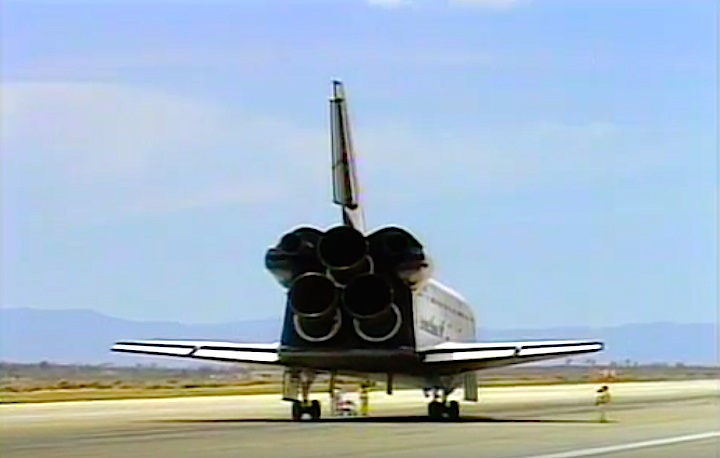
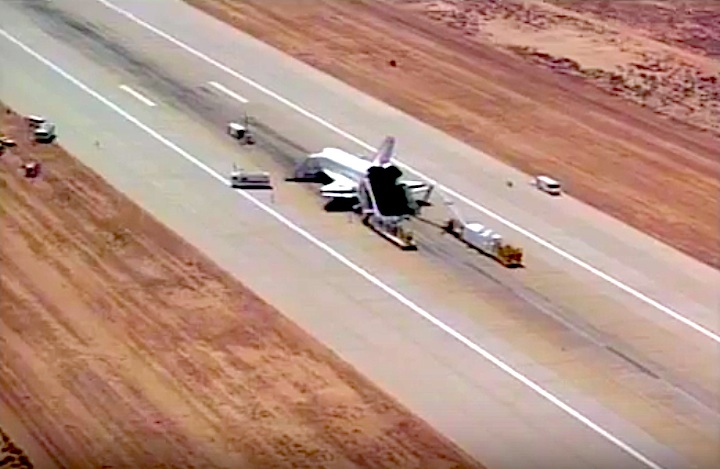
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
Landing: May 8, 1989, 12:43:26 p.m. PDT
Landing Weight: 194,789 pounds
Runway: 22
Rollout Distance: 10,295 feet
Rollout Time: 64 seconds
Revolution: 65
Mission Duration: 4 days, 0 hours, 56 minutes, 27 seconds
Returned to KSC: May 15, 1989
Orbit Altitude: 184 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 28.8 degrees
Miles Traveled: 1.7 million
Crew Members

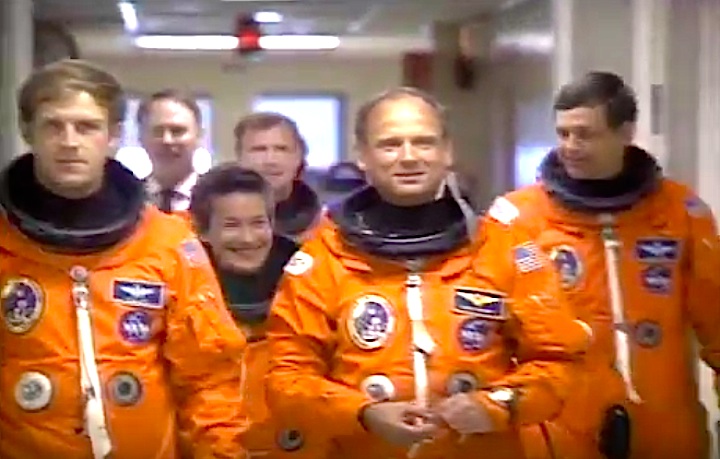
Image above: STS-30 Crew photo with Commander David M. Walker, Pilot Ronald J. Grabe, Mission Specialists Norman E. Thagard, Mary L. Cleave and Mark C. Lee. Image Credit: NASA
Launch Highlights
 The launch scheduled for April 28 was scrubbed at T-31 seconds due to a problem with the liquid hydrogen recirculation pump on the number one main engine and a vapor leak in a four-inch liquid hydrogen recirculation line between the orbiter and the external tank. The repairs were made and launch was reset for May 4. Liftoff was delayed until the last five minutes of a 64 minute window opening at 1:48 a.m. EDT due to cloud cover and high winds at KSC shuttle runway, violating return-to-launch-site limits.
The launch scheduled for April 28 was scrubbed at T-31 seconds due to a problem with the liquid hydrogen recirculation pump on the number one main engine and a vapor leak in a four-inch liquid hydrogen recirculation line between the orbiter and the external tank. The repairs were made and launch was reset for May 4. Liftoff was delayed until the last five minutes of a 64 minute window opening at 1:48 a.m. EDT due to cloud cover and high winds at KSC shuttle runway, violating return-to-launch-site limits. Mission Highlights
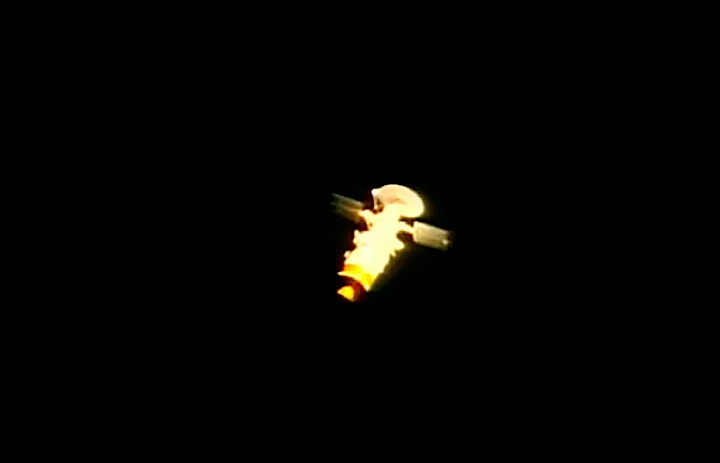
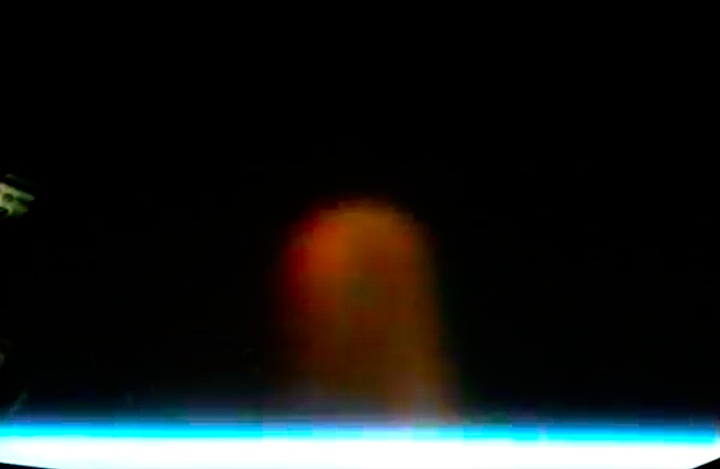
The primary payload, a Magellan/Venus radar mapper spacecraft and attached Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), was deployed six hours, 14 minutes into flight. The IUS first and second stage fired as planned, boosting the Magellan spacecraft on a proper trajectory for a 15-month journey to Venus.
Secondary payloads were: Mesoscale Lightning Experiment (MLE), microgravity research with Fluids Experiment Apparatus (FEA), and Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS) experiment.
One of five General Purpose Computers (GPC) failed and had to be replaced with a sixth onboard hardware spare. This is the first time a GPC was switched on orbit.
---

STS-30 | Shuttle: Atlantis | Launch: May 4, 1989
Seated from left to right: Ronald J. Grabe (pilot), Norman E. Thagard (mission specialist), Mark C. Lee (mission specialist), Standing from left to right: David M. Walker (commander), Mary L. Cleave (mission specialist)
Seated from left to right: Ronald J. Grabe (pilot), Norman E. Thagard (mission specialist), Mark C. Lee (mission specialist), Standing from left to right: David M. Walker (commander), Mary L. Cleave (mission specialist)


STS-30
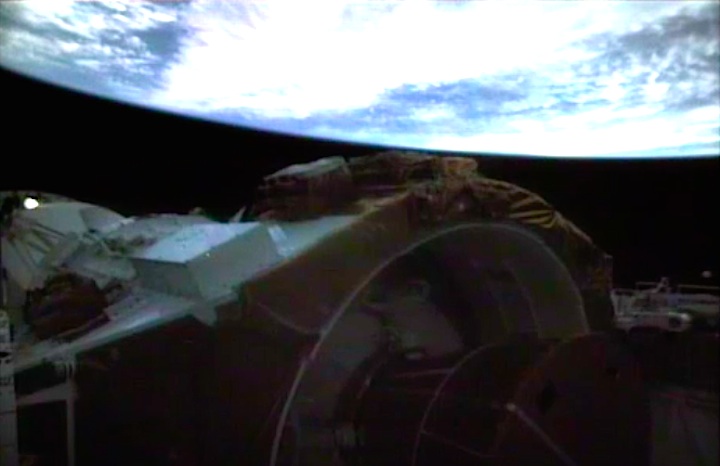
STS-30 Magellan spacecraft & IUS deployment from Atlantis' payload bay (PLB)
Credit: NASA
STS-30 Magellan spacecraft & IUS deployment from Atlantis' payload bay (PLB)
Credit: NASA

Mounted atop Boeing’s Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), the Magellan spacecraft departs Atlantis’ payload bay on 4 May 1989, 25 years ago today. Photo Credit: NASA
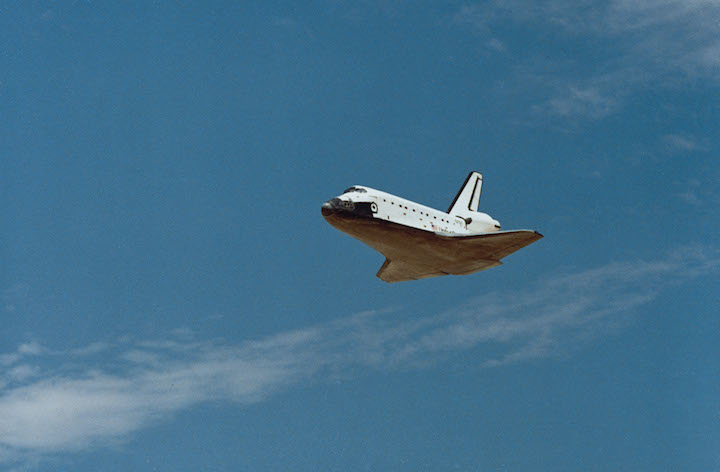

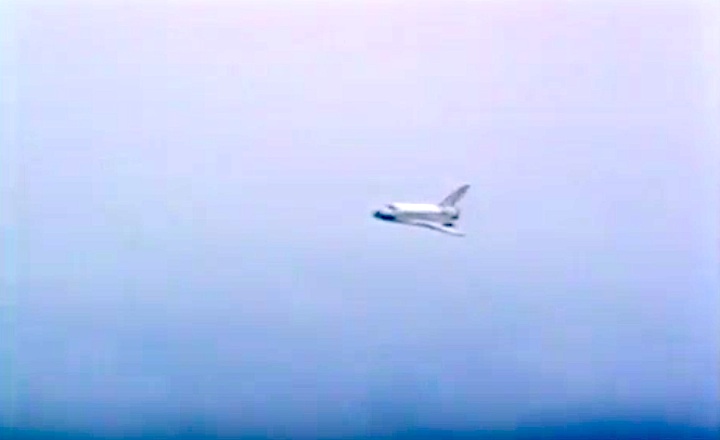
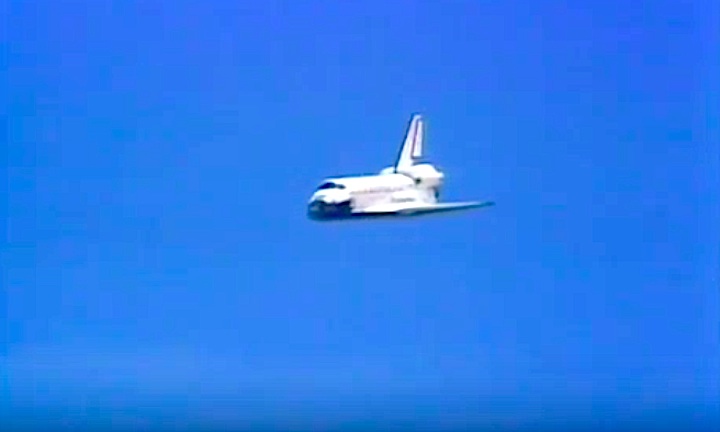
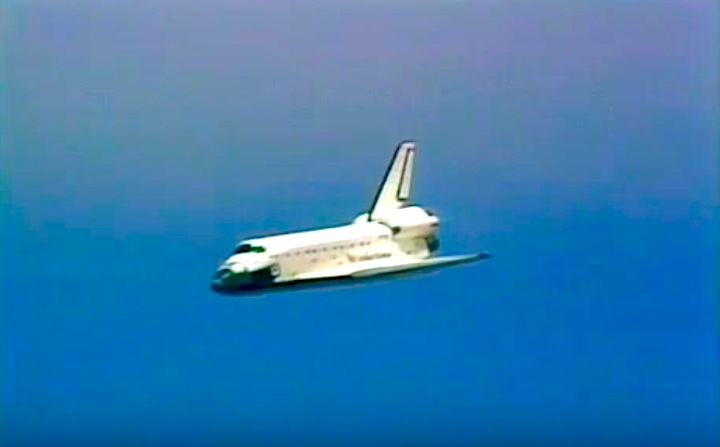
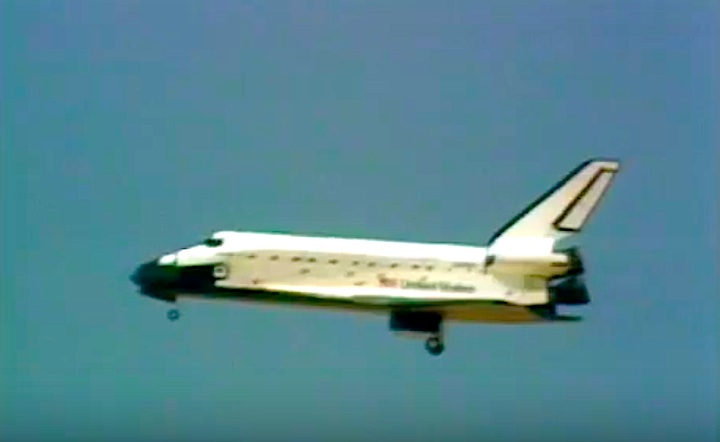
STS030-S-126 (8 May 1989) --- The space shuttle Atlantis, as seen in a low angle view on its glide in from Earth orbit, heads toward a concrete runway at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Onboard were astronauts David M. Walker, STS-30 commander; Ronald J. Grabe, pilot; and astronauts Norman E. Thagard, Mary L. Cleave and Mark C. Lee -- all mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA
---
Frams von STS-30 Atlantis Mission NASA-Video:
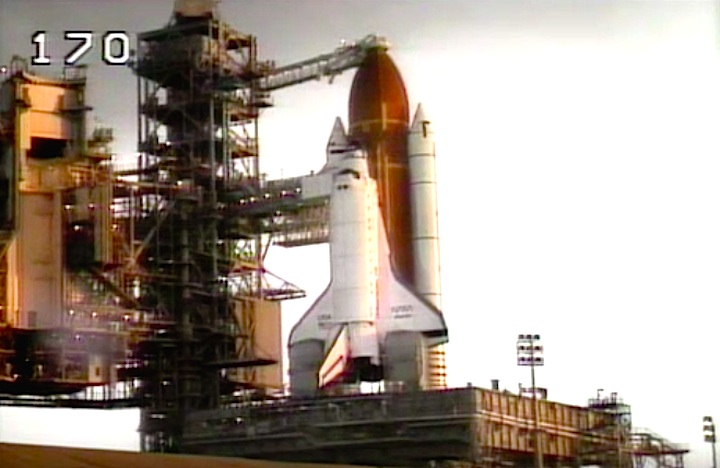
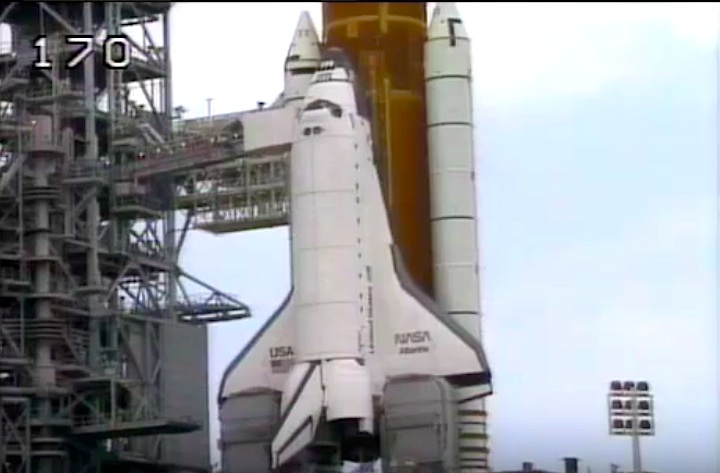
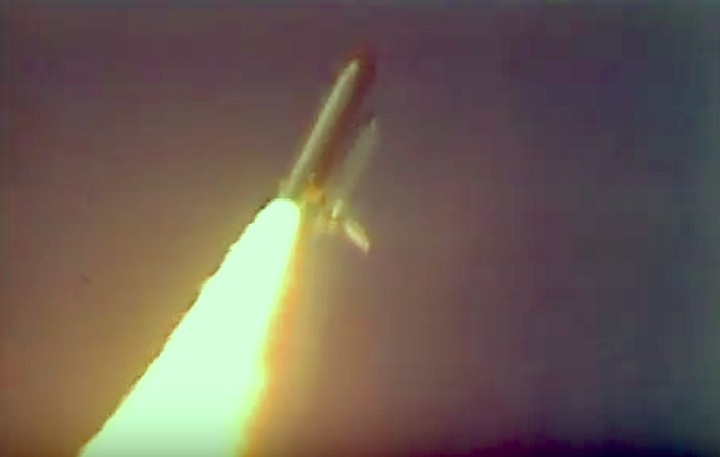
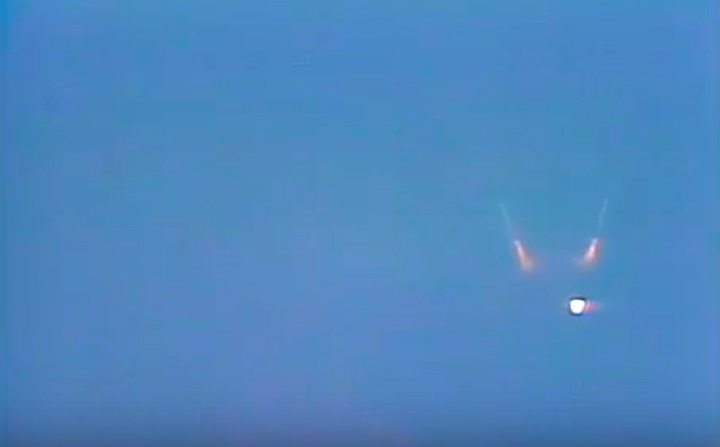













































Magellan-Sonde auf dem Weg zur Venus...
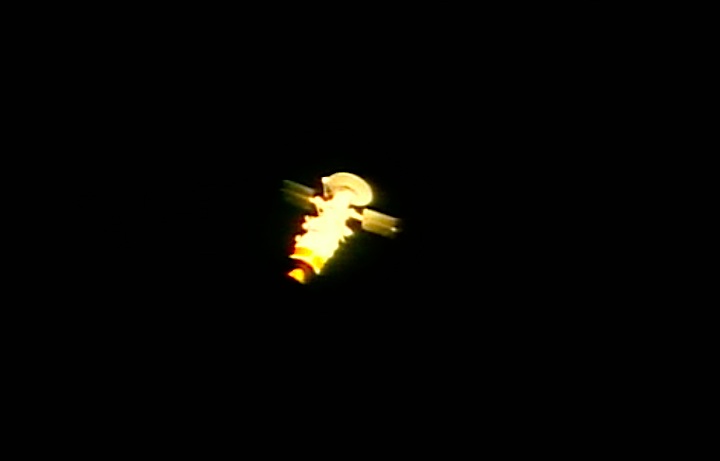
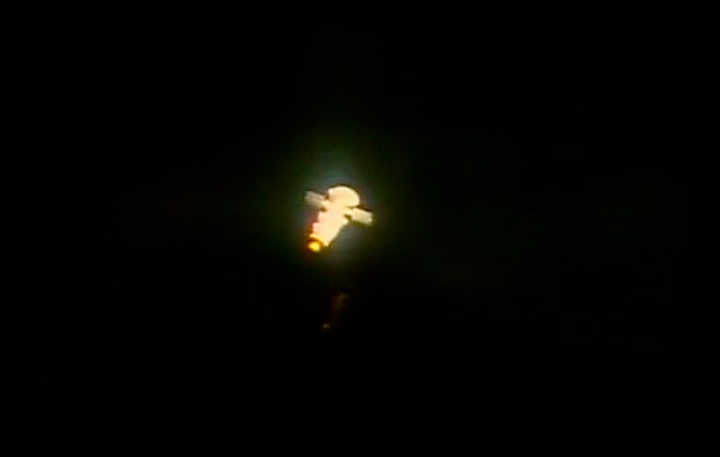


























Steuerdüsen-Einsatz...




























Quelle: NASA
3743 Views
