.

STS-26
Mission: TDRS-C
Space Shuttle: Discovery
Launch Pad: 39B
Launch Weight: 254,606 pounds
Launched: Sept. 29, 1988, 11:37:00 a.m. EDT
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
Landing: October 3, 1988, 9:37:11 a.m. PDT
Landing Weight: 194,184 pounds
Runway: 17
Rollout Distance: 7,451 feet
Rollout Time: 46 seconds
Revolution: 64
Mission Duration: 4 days, 1 hour, 0 minutes, 11 seconds
Returned to KSC: Oct. 8, 1988
Orbit Altitude: 203 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 28.5 degrees
Miles Traveled: 1.7 million
Crew Members
-
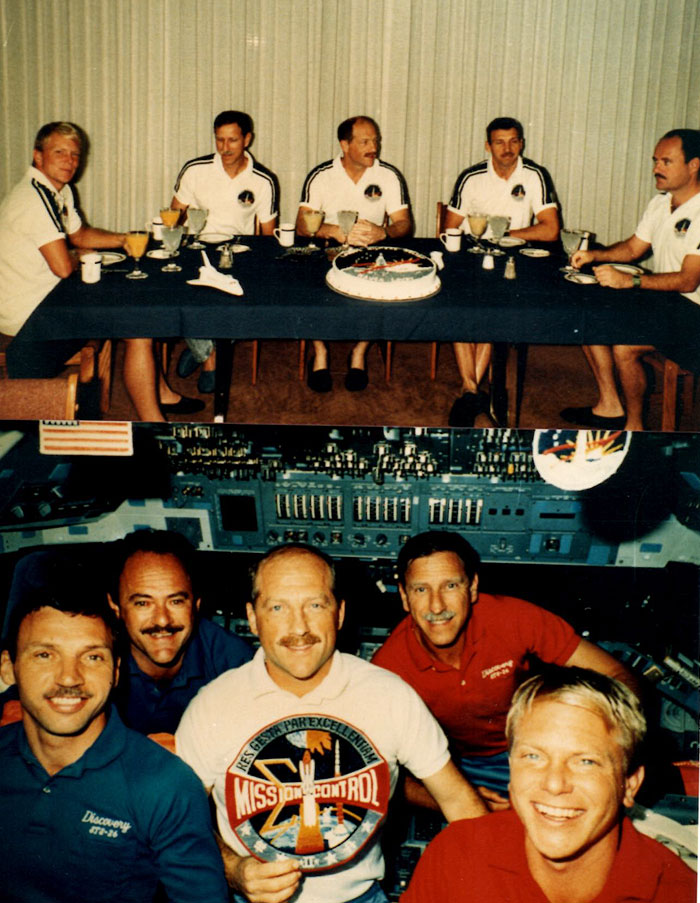

STS-26 Crew photo with Commander Frederick H. Hauck, Pilot Richard O. Covey, Mission Specialists John M. Lounge, George D. Nelson and David C. Hilmers. Image Credit: NASA
Launch Highlights
STS-26 Mission Patch The launch was delayed 1 hour, 38 minutes to replace fuses in the cooling system of two of the crew's flight pressure suits, and due to lighter than expected upper atmospheric winds. The suit repairs were successful and the countdown continued after a waiver of wind condition constraint was issued.
Mission Highlights
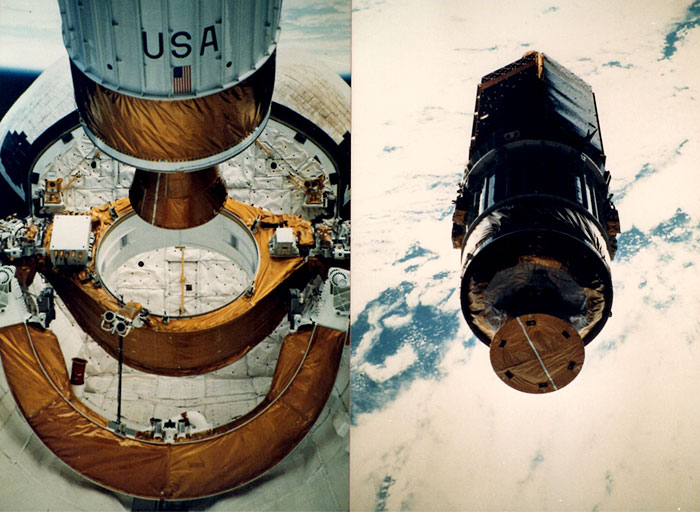
The primary payload, NASA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-3 (TDRS-3) attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), became the second TDRS deployed. After deployment, IUS propelled the satellite to a geosynchronous orbit. Secondary payloads: Physical Vapor Transport of Organic Solids (PVTOS); Protein Crystal Growth (PCG); Infrared Communications Flight Experiment (IRCFE); Aggregation of Red Blood Cells (ARC); Isoelectric Focusing Experiment (IFE); Mesoscale Lightning Experiment (MLE); Phase Partitioning Experiment (PPE); Earth-Limb Radiance Experiment (ELRAD); Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (ADSF) and two Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSIP) experiments. Orbiter Experiments Autonomous Supporting Instrumentation System-I (OASIS-I) recorded variety of environmental measurements during various inflight phases of orbiter.
Ku-band antenna in the payload bay was deployed; however, the dish antenna command and actual telemetry did not correspond. Also, the orbiter cabin Flash Evaporator System iced up, raising crew cabin temperature to the mid-80s.
.

-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
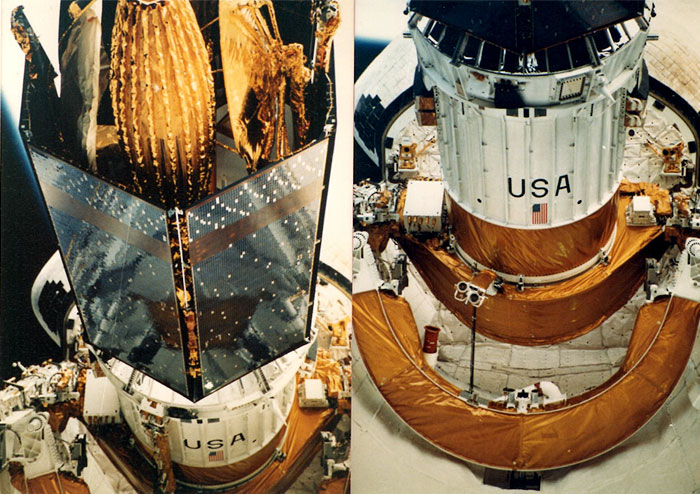
NASA Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-3 (TDRS-3)
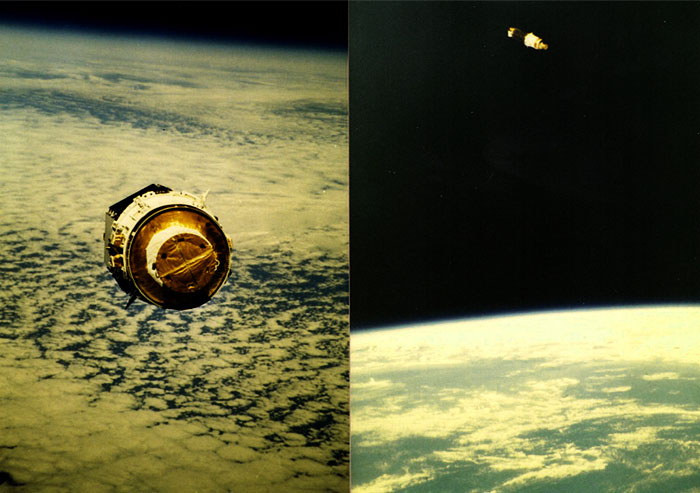
-

-


NASA
Quelle: CENAP-Archiv
3576 Views
