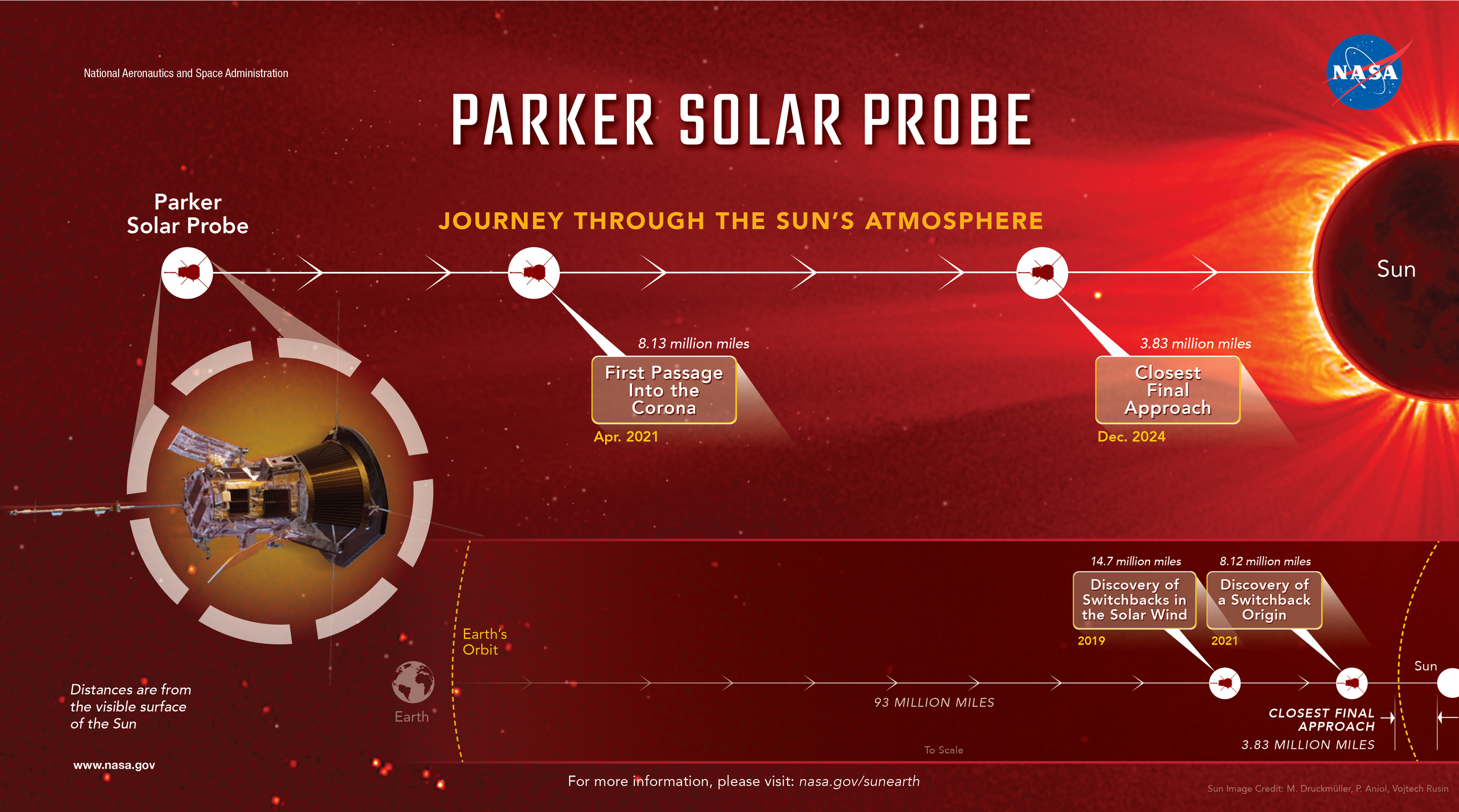
28.12.2024
Nasa makes history with closest-ever approach to Sun
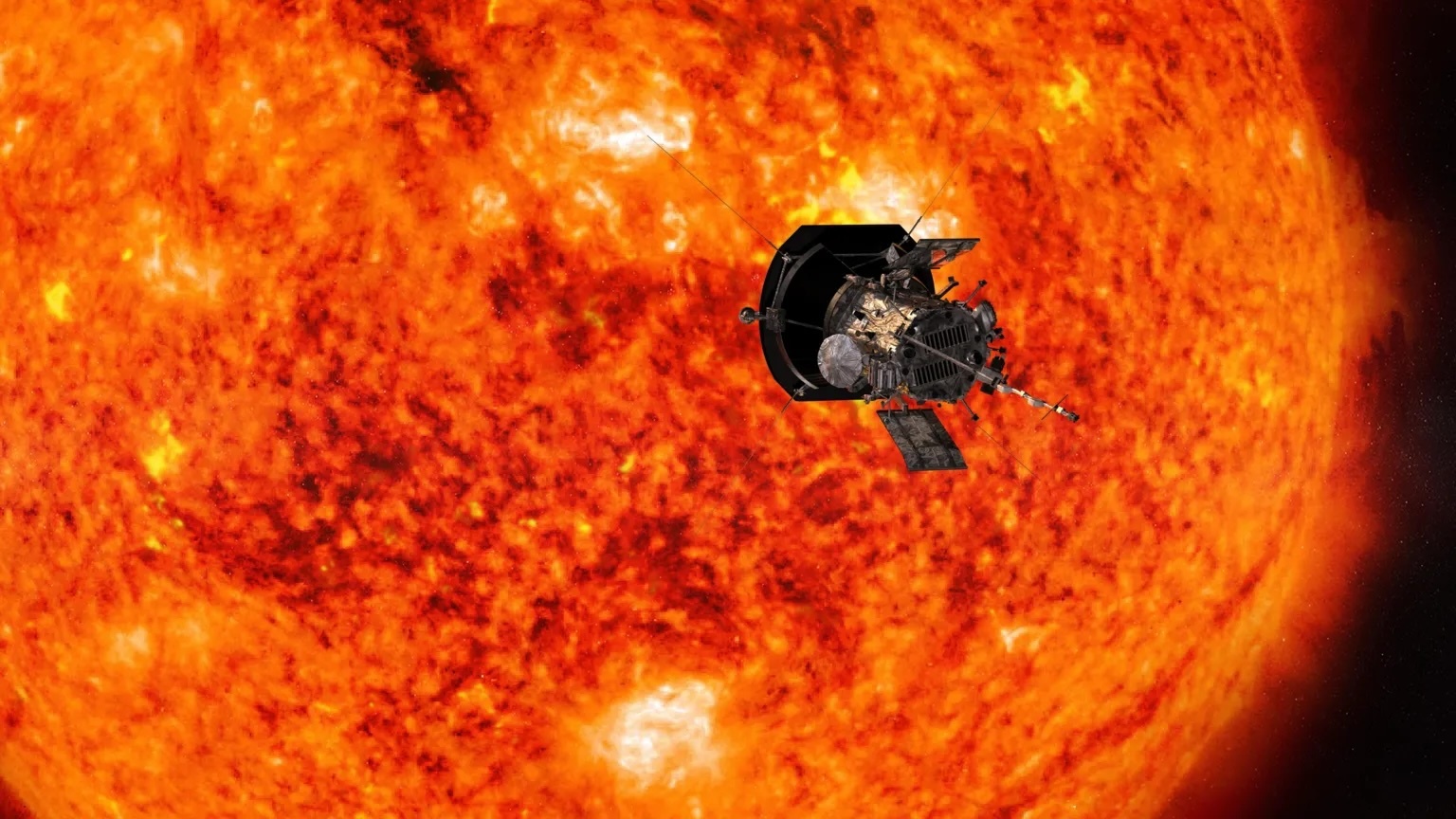

A Nasa spacecraft has made history by surviving the closest-ever approach to the Sun.
Scientists received a signal from the Parker Solar Probe just before midnight EST on Thursday (05:00 GMT on Friday) after it had been out of communication for several days during its burning-hot fly-by.
Nasa said the probe was "safe" and operating normally after it passed just 3.8 million miles (6.1 million km) from the solar surface.
The probe plunged into our star's outer atmosphere on Christmas Eve, enduring brutal temperatures and extreme radiation in a quest to better our understanding of how the Sun works.
Nasa then waited nervously for a signal, which had been expected at 05:00 GMT on 28 December.
Moving at up to 430,000 mph (692,000 kph), the spacecraft endured temperatures of up to 1,800F (980C), according to the Nasa website.
"This close-up study of the Sun allows Parker Solar Probe to take measurements that help scientists better understand how material in this region gets heated to millions of degrees, trace the origin of the solar wind (a continuous flow of material escaping the Sun), and discover how energetic particles are accelerated to near light speed," the agency said.
Dr Nicola Fox, head of science at Nasa, previously told BBC News: "For centuries, people have studied the Sun, but you don't experience the atmosphere of a place until you actually go [and] visit it.
"And so we can't really experience the atmosphere of our star unless we fly through it."
Parker Solar Probe launched in 2018, heading to the centre of our solar system.
It had already swept past the Sun 21 times, getting ever nearer, but the Christmas Eve visit was record-breaking.
At its closest approach, the probe was 3.8 million miles (6.1 million km) from our star's surface.
That might not sound that close, but Dr Fox put it into perspective. "We are 93 million miles away from the Sun, so if I put the Sun and the Earth one metre apart, Parker Solar Probe is 4cm from the Sun - so that's close."
The probe endured temperatures of 1,400C and radiation that could have frazzled the on-board electronics.
It was protected by an 11.5cm (4.5in) thick carbon-composite shield, but the spacecraft's tactic was to get in and out fast.
In fact, it moved faster than any human-made object, hurtling at 430,000mph - the equivalent of flying from London to New York in less than 30 seconds.
Parker's speed came from the immense gravitational pull it felt as it fell towards the Sun.

So why go to all this effort to "touch" the Sun?
Scientists hope that as the spacecraft passed through our star's outer atmosphere - its corona - it will have collected data that will solve a long-standing mystery.
"The corona is really, really hot, and we have no idea why," explained Dr Jenifer Millard, an astronomer at Fifth Star Labs in Wales.
"The surface of the Sun is about 6,000C or so, but the corona, this tenuous outer atmosphere that you can see during solar eclipses, reaches millions of degrees - and that is further away from the Sun. So how is that atmosphere getting hotter?"
The mission should also help scientists better understand solar wind - the constant stream of charged particles bursting out from the corona.
When these particles interact with the Earth's magnetic field the sky lights up with dazzling auroras.
But this so-called space weather can cause problems too, knocking out power grids, electronics and communication systems.
"Understanding the Sun, its activity, space weather, the solar wind, is so important to our everyday lives on Earth," said Dr Millard.
Nasa scientists faced an anxious wait over Christmas while the spacecraft was out of touch with Earth.
Dr Fox had been expecting the team to text her a green heart to let her know the probe was OK as soon as a signal was beamed back home.
She previously admitted she was nervous about the audacious attempt, but had faith in the probe.
"I will worry about the spacecraft. But we really have designed it to withstand all of these brutal, brutal conditions. It's a tough, tough little spacecraft."
Quelle: BBC
----
Update: 29.12.2024
.

Operations teams have confirmed NASA’s mission to “touch” the Sun survived its record-breaking closest approach to the solar surface on Dec. 24, 2024.
Breaking its previous record by flying just 3.8 million miles above the surface of the Sun, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe hurtled through the solar atmosphere at a blazing 430,000 miles per hour — faster than any human-made object has ever moved. A beacon tone received late on Dec. 26 confirmed the spacecraft had made it through the encounter safely and is operating normally.
This pass, the first of more to come at this distance, allows the spacecraft to conduct unrivaled scientific measurements with the potential to change our understanding of the Sun.
Flying this close to the Sun is a historic moment in humanity’s first mission to a star.

NICKY FOX
NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate
"Flying this close to the Sun is a historic moment in humanity’s first mission to a star,” said Nicky Fox, who leads the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “By studying the Sun up close, we can better understand its impacts throughout our solar system, including on the technology we use daily on Earth and in space, as well as learn about the workings of stars across the universe to aid in our search for habitable worlds beyond our home planet.”
Credits: NASA
This video can be freely shared and downloaded at https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14741.
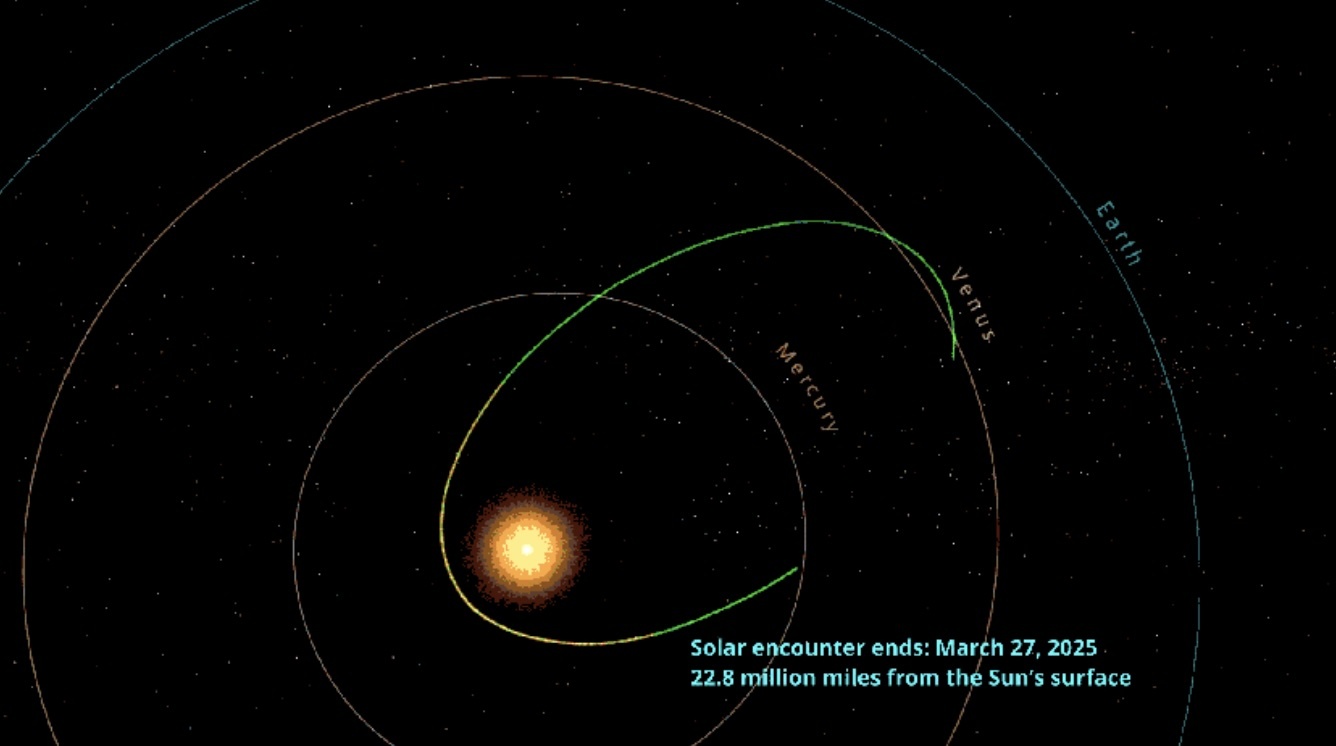
Parker Solar Probe has spent the last six years setting up for this moment. Launched in 2018, the spacecraft used seven flybys of Venus to gravitationally direct it ever closer to the Sun. With its last Venus flyby on Nov. 6, 2024, the spacecraft reached its optimal orbit. This oval-shaped orbit brings the spacecraft an ideal distance from the Sun every three months — close enough to study our Sun’s mysterious processes but not too close to become overwhelmed by the Sun’s heat and damaging radiation. The spacecraft will remain in this orbit for the remainder of its primary mission.
“Parker Solar Probe is braving one of the most extreme environments in space and exceeding all expectations,” said Nour Rawafi, the project scientist for Parker Solar Probe at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), which designed, built, and operates the spacecraft from its campus in Laurel, Maryland. “This mission is ushering a new golden era of space exploration, bringing us closer than ever to unlocking the Sun’s deepest and most enduring mysteries.”
Close to the Sun, the spacecraft relies on a carbon foam shield to protect it from the extreme heat in the upper solar atmosphere called the corona, which can exceed 1 million degrees Fahrenheit. The shield was designed to reach temperatures of 2,600 degrees Fahrenheit — hot enough to melt steel — while keeping the instruments behind it shaded at a comfortable room temperature. In the hot but low-density corona, the spacecraft’s shield is expected to warm to 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
“It’s monumental to be able to get a spacecraft this close to the Sun,” said John Wirzburger, the Parker Solar Probe mission systems engineer at APL. “This is a challenge the space science community has wanted to tackle since 1958 and had spent decades advancing the technology to make it possible.”
By flying through the solar corona, Parker Solar Probe can take measurements that help scientists better understand how the region gets so hot, trace the origin of the solar wind (a constant flow of material escaping the Sun), and discover how energetic particles are accelerated to half the speed of light.
“The data is so important for the science community because it gives us another vantage point,” said Kelly Korreck, a program scientist at NASA Headquarters and heliophysicist who worked on one of the mission’s instruments. “By getting firsthand accounts of what’s happening in the solar atmosphere, Parker Solar Probe has revolutionized our understanding of the Sun.”
Previous passes have already aided scientists’ understanding of the Sun. When the spacecraft first passed into the solar atmosphere in 2021, it found the outer boundary of the corona is wrinkled with spikes and valleys, contrary to what was expected. Parker Solar Probe also pinpointed the origin of important zig-zag-shaped structures in the solar wind, called switchbacks, at the visible surface of the Sun — the photosphere.
Since that initial pass into the Sun, the spacecraft has been spending more time in the corona, where most of the critical physical processes occur.
“We now understand the solar wind and its acceleration away from the Sun,” said Adam Szabo, the Parker Solar Probe mission scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “This close approach will give us more data to understand how it’s accelerated closer in.”
Parker Solar Probe has also made discoveries across the inner solar system. Observations showed how giant solar explosions called coronal mass ejections vacuum up dust as they sweep across the solar system, and other observations revealed unexpected findings about solar energetic particles. Flybys of Venus have documented the planet’s natural radio emissions from its atmosphere, as well as the first complete image of its orbital dust ring.
So far, the spacecraft has only transmitted that it’s safe, but soon it will be in a location that will allow it to downlink the data it collected on this latest solar pass.
The data that will come down from the spacecraft will be fresh information about a place that we, as humanity, have never been.

JOE WESTLAKE
Heliophysics Division Director, NASA Headquarters
“The data that will come down from the spacecraft will be fresh information about a place that we, as humanity, have never been,” said Joe Westlake, the director of the Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters. “It’s an amazing accomplishment.”
The spacecraft’s next planned close solar passes come on March 22, 2025, and June 19, 2025.
A NASA spacecraft will make another close pass of the sun
A NASA spacecraft will make its second close brush with the sun
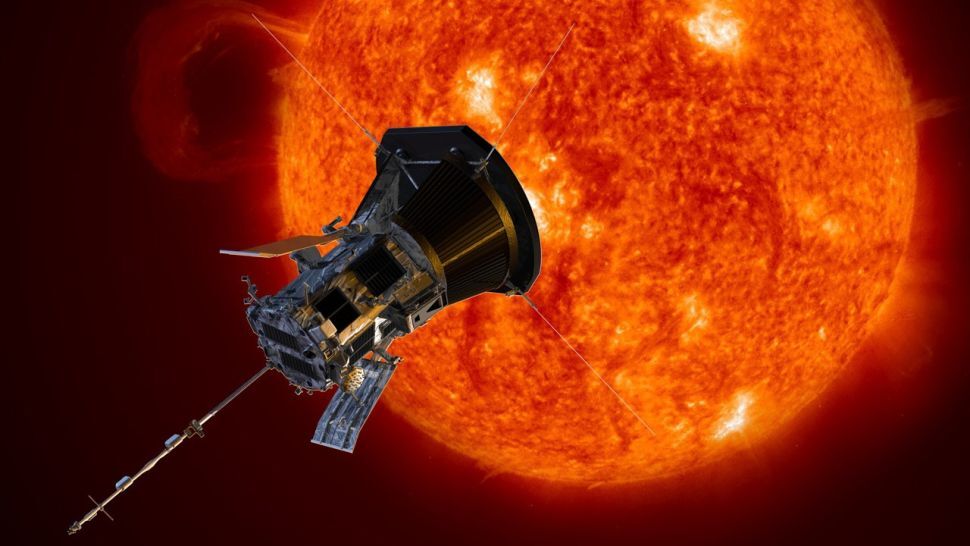

A NASA spacecraft will make another close brush with the sun, the second of three planned encounters through the sizzling solar atmosphere.
The Parker Solar Probe made its record-breaking first pass within 3.8 million miles (6 million kilometers) of the scorching sun in December, flying closer than any object sent before.
Plans called for it to attempt that journey again on Saturday. Since the flyby happens out of communication range, the mission team won't hear back from Parker until Tuesday afternoon.
Parker is the fastest spacecraft built by humans, and is once again set to hit 430,000 mph (690,000 kph) at closest approach.
Launched in 2018 to get a close-up look at the sun, Parker has since flown straight through its crownlike outer atmosphere, or corona.
Scientists hope the data from Parker will help them better understand why the sun’s outer atmosphere is hundreds of times hotter than its surface and what drives the solar wind, the supersonic stream of charged particles constantly blasting away from the sun.
Quelle: abcNews
----
Update: 25.06.2025
.
Parker Solar Probe Completes 24th Close Approach to Sun
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe completed its 24th close approach to the Sun on Thursday, June 19, matching its record distance of 3.8 million miles (6.2 million kilometers) from the solar surface. Following this flyby — the last of the spacecraft’s baseline mission plan — Parker Solar Probe will remain in orbit around the Sun and continue making observations until next steps for the mission are formally reviewed in 2026.
Parker Solar Probe checked in with mission operators at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Maryland — where it was also designed and built — on Sunday, June 22, reporting that all systems are healthy and operating normally. The spacecraft was out of contact with Earth and operating autonomously during the close approach.
During this flyby, the spacecraft also equaled its record-setting speed of 430,000 miles per hour (687,000 km per hour) — a mark that, like the distance, was set and subsequently matched during close approaches on Dec. 24, 2024, and March 22, 2025.
This close to the Sun, the spacecraft relied on its innovative carbon foam shield, known simply as the Thermal Protection System, to protect itself from the intense heat. Spacecraft operators expect the shield faced temperatures of between 1,600 to 1,700 F (870 to 930 C) at closest approach.
During the solar encounter — which began June 14 and ends June 24 — Parker’s four scientific instrument packages are gathering unique observations from inside the Sun’s corona. The flyby, as the third at this distance and speed, is allowing the spacecraft to conduct unrivaled measurements of the solar wind and solar activity while the Sun is in a more active phase of its 11-year cycle.
Parker’s observations of the solar wind and solar events, such as flares and coronal mass ejections, are critical to advancing humankind’s understanding of the Sun and the phenomena that drive high-energy space weather events that pose risks to astronauts, satellites, air travel and even power grids on Earth. Understanding the fundamental physics of space weather enables more reliable prediction of astronaut safety during future deep-space missions to the Moon and Mars.
“Parker Solar Probe remains in excellent health, with both the spacecraft and its instruments ready to continue their groundbreaking mission,” said Arik Posner, Parker Solar Probe program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “The spacecraft will keep exploring the solar atmosphere as the Sun enters the declining phase of its 11-year cycle, providing a unique opportunity to study how solar activity evolves and shapes the heliosphere during this pivotal period.”
Parker Solar Probe was developed as a part of NASA’s Living With a Star (LWS) program to explore aspects of the Sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. The LWS program is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. APL manages Parker Solar Probe for NASA and designed, built, and operates the mission.
Quelle: NASA
----
Update: 12.07.2025
.
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe Snaps Closest-Ever Images to Sun
KEY POINTS
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has taken the closest ever images to the Sun, captured just 3.8 million miles from the solar surface.
- The new close-up images show features in the solar wind, the constant stream of electrically charged subatomic particles released by the Sun that rage across the solar system at speeds exceeding 1 million miles an hour.
- These images, and other data, are helping scientists understand the mysteries of the solar wind, which is essential to understanding its effects at Earth.
On its record-breaking pass by the Sun late last year, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe captured stunning new images from within the Sun’s atmosphere. These newly released images — taken closer to the Sun than we’ve ever been before — are helping scientists better understand the Sun’s influence across the solar system, including events that can affect Earth.
“Parker Solar Probe has once again transported us into the dynamic atmosphere of our closest star,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “We are witnessing where space weather threats to Earth begin, with our eyes, not just with models. This new data will help us vastly improve our space weather predictions to ensure the safety of our astronauts and the protection of our technology here on Earth and throughout the solar system.”
Parker Solar Probe started its closest approach to the Sun on Dec. 24, 2024, flying just 3.8 million miles from the solar surface. As it skimmed through the Sun’s outer atmosphere, called the corona, in the days around the perihelion, it collected data with an array of scientific instruments, including the Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe, or WISPR.
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Joy Ng
The new WISPR images reveal the corona and solar wind, a constant stream of electrically charged particles from the Sun that rage across the solar system. The solar wind expands throughout of the solar system with wide-ranging effects. Together with outbursts of material and magnetic currents from the Sun, it helps generate auroras, strip planetary atmospheres, and induce electric currents that can overwhelm power grids and affect communications at Earth. Understanding the impact of solar wind starts with understanding its origins at the Sun.
The WISPR images give scientists a closer look at what happens to the solar wind shortly after it is released from the corona. The images show the important boundary where the Sun’s magnetic field direction switches from northward to southward, called the heliospheric current sheet. It also captures the collision of multiple coronal mass ejections, or CMEs — large outbursts of charged particles that are a key driver of space weather — for the first time in high resolution.
“In these images, we’re seeing the CMEs basically piling up on top of one another,” said Angelos Vourlidas, the WISPR instrument scientist at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, which designed, built, and operates the spacecraft in Laurel, Maryland. “We’re using this to figure out how the CMEs merge together, which can be important for space weather.”
When CMEs collide, their trajectory can change, making it harder to predict where they’ll end up. Their merger can also accelerate charged particles and mix magnetic fields, which makes the CMEs’ effects potentially more dangerous to astronauts and satellites in space and technology on the ground. Parker Solar Probe’s close-up view helps scientists better prepare for such space weather effects at Earth and beyond.
Zooming in on Solar Wind’s Origins
The solar wind was first theorized by preeminent heliophysicist Eugene Parker in 1958. His theories about the solar wind, which were met with criticism at the time, revolutionized how we see our solar system. Prior to Parker Solar Probe’s launch in 2018, NASA and its international partners led missions like Mariner 2, Helios, Ulysses, Wind, and ACE that helped scientists understand the origins of the solar wind — but from a distance. Parker Solar Probe, named in honor of the late scientist, is filling in the gaps of our understanding much closer to the Sun.
At Earth, the solar wind is mostly a consistent breeze, but Parker Solar Probe found it’s anything but at the Sun. When the spacecraft reached within 14.7 million miles from the Sun, it encountered zig-zagging magnetic fields — a feature known as switchbacks. Using Parker Solar Probe’s data, scientists discovered that these switchbacks, which came in clumps, were more common than expected.
When Parker Solar Probe first crossed into the corona about 8 million miles from the Sun’s surface in 2021, it noticed the boundary of the corona was uneven and more complex than previously thought.
As it got even closer, Parker Solar Probe helped scientists pinpoint the origin of switchbacks at patches on the visible surface of the Sun where magnetic funnels form. In 2024 scientists announced that the fast solar wind — one of two main classes of the solar wind — is in part powered by these switchbacks, adding to a 50-year-old mystery.
However, it would take a closer view to understand the slow solar wind, which travels at just 220 miles per second, half the speed of the fast solar wind.
“The big unknown has been: how is the solar wind generated, and how does it manage to escape the Sun’s immense gravitational pull?” said Nour Rawafi, the project scientist for Parker Solar Probe at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. “Understanding this continuous flow of particles, particularly the slow solar wind, is a major challenge, especially given the diversity in the properties of these streams — but with Parker Solar Probe, we’re closer than ever to uncovering their origins and how they evolve.”
Understanding Slow Solar Wind
The slow solar wind, which is twice as dense and more variable than fast solar wind, is important to study because its interplay with the fast solar wind can create moderately strong solar storm conditions at Earth sometimes rivaling those from CMEs.
Prior to Parker Solar Probe, distant observations suggested there are actually two varieties of slow solar wind, distinguished by the orientation or variability of their magnetic fields. One type of slow solar wind, called Alfvénic, has small-scale switchbacks. The second type, called non-Alfvénic, doesn’t show these variations in its magnetic field.
As it spiraled closer to the Sun, Parker Solar Probe confirmed there are indeed two types. Its close-up views are also helping scientists differentiate the origins of the two types, which scientists believe are unique. The non-Alfvénic wind may come off features called helmet streamers — large loops connecting active regions where some particles can heat up enough to escape — whereas Alfvénic wind might originate near coronal holes, or dark, cool regions in the corona.
In its current orbit, bringing the spacecraft just 3.8 million miles from the Sun, Parker Solar Probe will continue to gather additional data during its upcoming passes through the corona to help scientists confirm the slow solar wind’s origins. The next pass comes Sept. 15, 2025.
“We don’t have a final consensus yet, but we have a whole lot of new intriguing data,” said Adam Szabo, Parker Solar Probe mission scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
Quelle: NASA

