30.07.2024
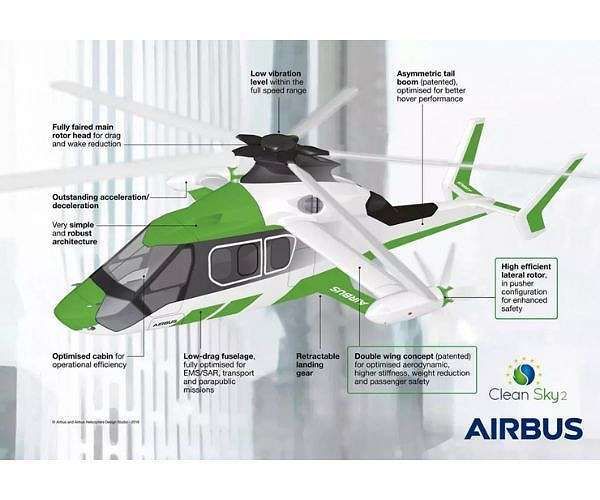
Airbus's Racer high-speed helicopter demonstrator, part of the European Research Clean Sky 2 project, has successfully achieved its fast cruise speed target of 407 km/h (220 kts). On June 21, less than two months after its maiden flight, the Racer demonstrator exceeded this target by reaching 420 km/h (227 kts) in its initial configuration. With only seven flights and around nine hours of flight testing, nearly the entire flight envelope has been explored.
"This achievement in such a short space of time is really a testimony to the hard work of our 40 partners in 13 European countries to bring all of this innovation to flight. On top of its performance, the aircraft's aerodynamic behavior and stability are promising. We are all looking forward to the next phase of flight testing, especially the eco-mode which will enable us to shut down one engine in forward flight, thus reducing fuel consumption, and lowering the CO2 emissions," said Bruno Even, CEO of Airbus Helicopters.
The flight test team included Herve Jammayrac, Chief Flight Test Pilot, Dominique Fournier, Flight Test Engineer, and Christophe Skorlic, Test Flight Engineer. The upcoming phase of flight testing will concentrate on single engine operations and completing the flight envelope assessment.
Optimized for a cruise speed exceeding 400 km/h, the Racer demonstrator aims to balance speed, cost-efficiency, and mission performance. The Racer also targets approximately 20% reduction in fuel consumption compared to current generation helicopters of the same maximum take-off weight category, thanks to aerodynamic enhancements and an innovative eco-mode propulsion system. Developed with Safran Helicopter Engines, the hybrid-electric eco-mode system allows one of the two Aneto-1X engines to be paused during cruise flight, thereby cutting CO2 emissions. Additionally, the Racer is designed to demonstrate how its unique architecture can lower its operational acoustic footprint.
Quelle: SD
