18.07.2024
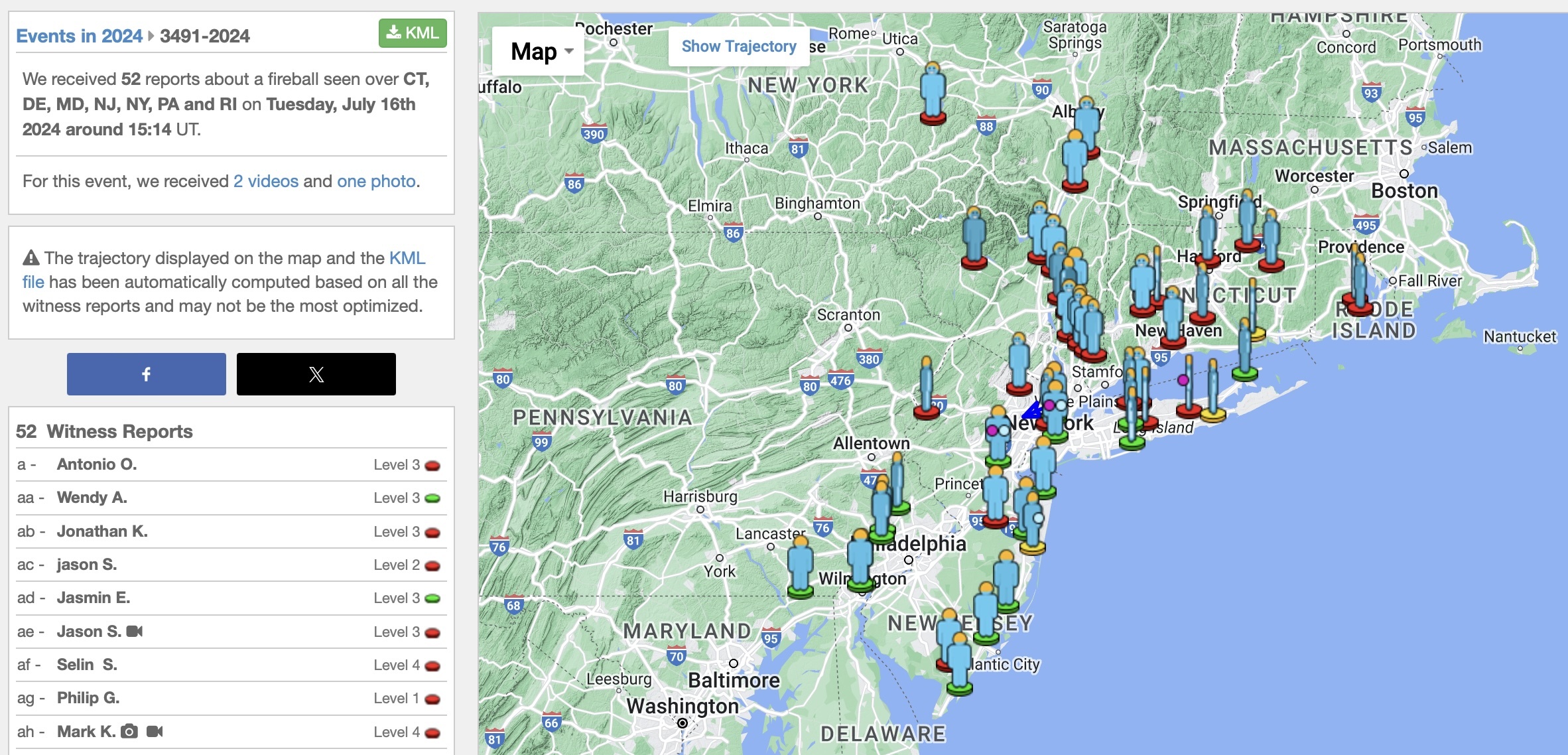
Over 40 eyewitness reports of the fireball were received by the American Meteor Society.

A meteor crashed into Earth's atmosphere over New York City yesterday (July 16), putting on quite the show for spectators throughout the region.
The meteor created a rare daytime fireball that traveled west into New Jersey at speeds of up to 38,000 mph (61,000 km/h) according to NASA Meteor Watch.
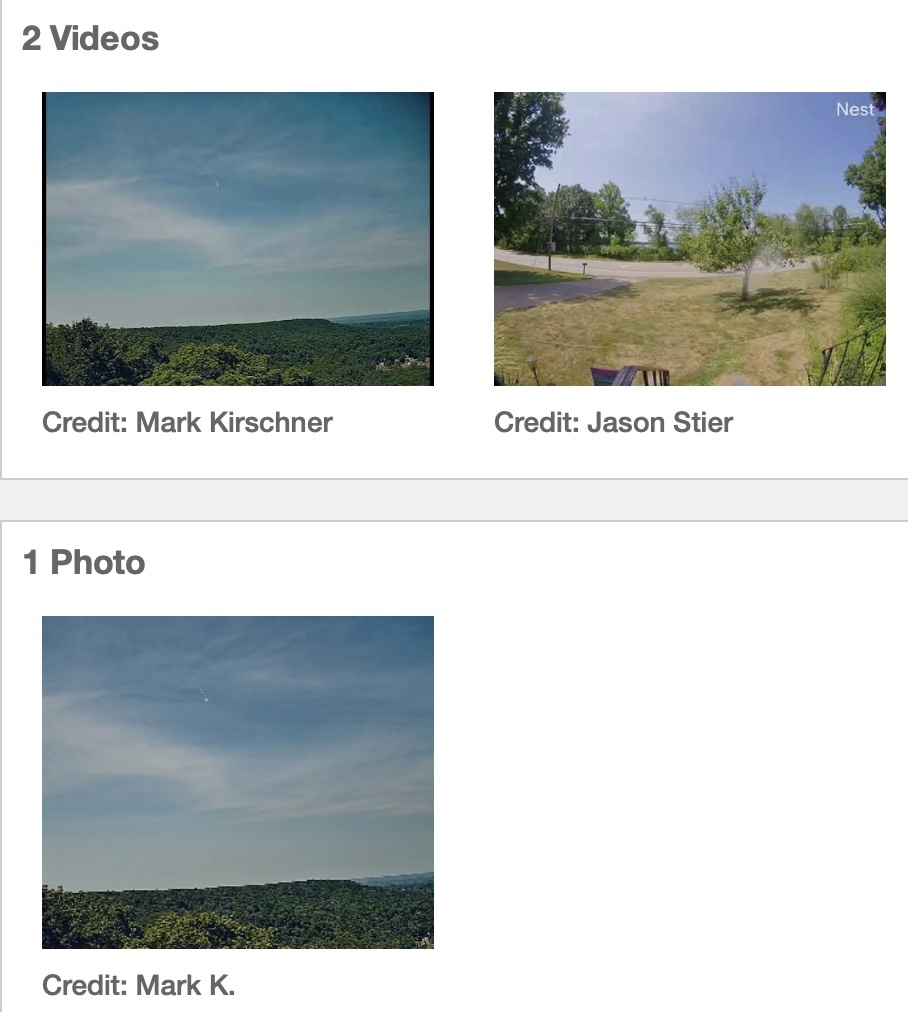
The American Meteor Society received several reports of a daytime fireball on July 16, 2024 over New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Delaware, Maryland, Rhode Island and Pennsylvania. Dramatic fireball footage was captured over Wayne, New Jersey and Northford, Connecticut.
Meteors are the visible trails of meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at high speeds, burning up as they travel through it. A fireball is an especially bright meteor with a visual magnitude of -3 or brighter when observed at the zenith. If a fireball explodes while moving through the atmosphere, it is called a bolide.

Earth is continuously bombarded by space rocks. NASA estimates that approximately 48.5 tons (44 metric tons) of material falls to Earth each day. Most of this material burns up in the atmosphere, occasionally creating "shooting stars" or fireballs. According to NASA, space rocks smaller than about 82 feet (25 meters) will likely burn up upon entering Earth's atmosphere, causing little to no damage.
The meteor that created the spectacular daytime fireball was likely around 1 foot (0.3 meters) in diameter and therefore incapable of surviving to the ground or posing any risk to Earth, according to NASA Meteor Watch.
Though loud booms and shaking were reported by some eyewitnesses, it remains unconfirmed whether or not the fireball was the culprit. According to NASA Meteor Watch, there were reports of military activity in the vicinity around the time of the fireball which would explain the loud sounds and shaking.
Quelle: SC
+++
Quelle: IMO
