20.12.2019
NASA says that SpaceX’s next big Crew Dragon flight test has slipped a bit further into 2020, a counterintuitively positive sign that the human-rated spacecraft’s next launch is firmly scheduled for the first month of the next decade.
Known as Crew Dragon’s In-Flight Abort (IFA) test, SpaceX opted to include the mission in its Commercial Crew contract, a decision NASA chose to leave up to its providers. Boeing, for example, chose not to perform a real-world in-flight abort test of its Starliner spacecraft, instead relying on a pad abort test and digital modeling to determine the spacecraft’s capabilities. NASA allowed this flexibility because it believes – at least theoretically – that it should be possible to determine whether a spacecraft can perform the most challenging abort scenarios without actually doing full-fidelity flight tests.
Given that NASA chose to perform an extremely expensive full-fidelity in-flight abort test with its own Orion spacecraft just a few months ago, one can’t exactly say that the space agency has chosen to reap what it’s sown, but with any luck, the Starliner spacecraft will never have to perform such an abort and find out how close Boeing’s modeling is to reality.
t’s also worth noting that despite the fact SpaceX elected to perform an extra abort test that will likely destroy an entire Falcon 9 rocket, Crew Dragon development will cost NASA $2 billion (40%) less than Starliner, while each operational Crew Dragon launch will also cost some $250 million (39%) less than a comparable Starliner launch.
As of December 18th, NASA says that SpaceX’s In-Flight Abort (IFA) test has slipped a week from January 4th to January 11th, 2020. Counterintuitively, that delay is actually an extremely encouraging sign that Crew Dragon’s next launch is quite firmly set for the first month of 2020. For reference, as NASA and SpaceX approached Crew Dragon’s Demo-1 orbital launch debut earlier this year, the mission was initially set for January 17th. Around three weeks later, NASA announced that Demo-1 had slipped to no earlier than (NET) “February”. Four weeks after that delay, NASA once again announced another delay to March 2nd, which would turn out to be the day that Crew Dragon really did reach orbit for the first time.
On the other hand, IFA – Crew Dragon’s second launch – had its first firm launch date (January 4th) announced by NASA on December 6th, 2019. Less than two weeks later, NASA says that the launch date has slipped by exactly one week to January 11th, less than four weeks from today. It’s entirely possible that SpaceX’s IFA test will slip further into 2020 in the coming weeks, but compared to Crew Dragon’s Demo-1 mission, both NASA and SpaceX appear to be far more confident in the schedule for Crew Dragon’s second launch.
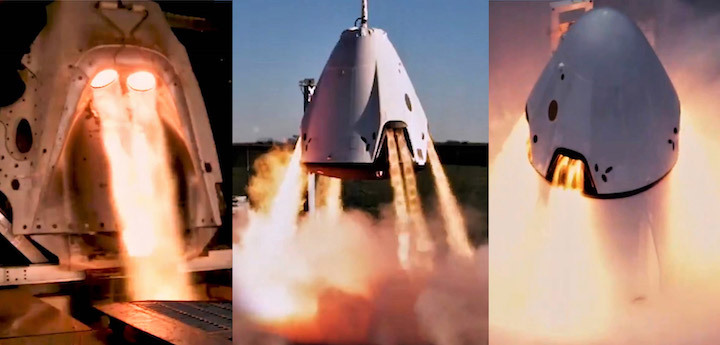
Regardless of when exactly it lifts off, Crew Dragon’s In-Flight Abort is going to be an extremely challenging test for the spacecraft. Designed to simulate a near-worst-case abort scenario during launch, SpaceX will essentially trick Dragon into believing that Falcon 9 has failed around a minute and a half after launch. At that point, the rocket and spacecraft will be traveling as fast as Mach 2.5 (860 m/s, 1900 mph) and experiencing what is known as Max Q, the point of peak aerodynamic stress (referring to heating, buffeting, pressure, and more).
At that exact point, Crew Dragon capsule C205 will ignite all eight of its SuperDraco abort engines, almost instantaneously producing 130,000 lbf (570 kN) of thrust to send the spacecraft almost a kilometer (0.5 mi) away from Falcon 9 in just a few seconds. If Crew Dragon survives the ordeal, it will quickly detach its trunk section, flip around to face its heat shield towards the ground, and ultimately deploy parachutes before gently landing in the Atlantic Ocean.
SpaceX plans to recover and reuse the otherwise orbit-worthy capsule on a future mission, likely one of the company’s upcoming CRS2 space station resupply launches. Finally, if everything goes exactly as planned during the In-Flight Abort test and both NASA and SpaceX see no issues with the flown hardware or data the test produces, Crew Dragon Demo-2 – the spacecraft’s first astronaut launch – could potentially be ready for flight as early as February or March 2020.
Quelle: TESLARATI
