24.05.2018
As the International Space Station flew over the Indonesian coast of Sumatra on an April night, lightning from a thunderstorm reached the upper layers of the atmosphere and its light show was captured by ESA’s latest observatory in space.
The Atmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor, also known as the Space Storm Hunter, is completing its initial tests a month after it was installed outside Europe’s Columbus laboratory.
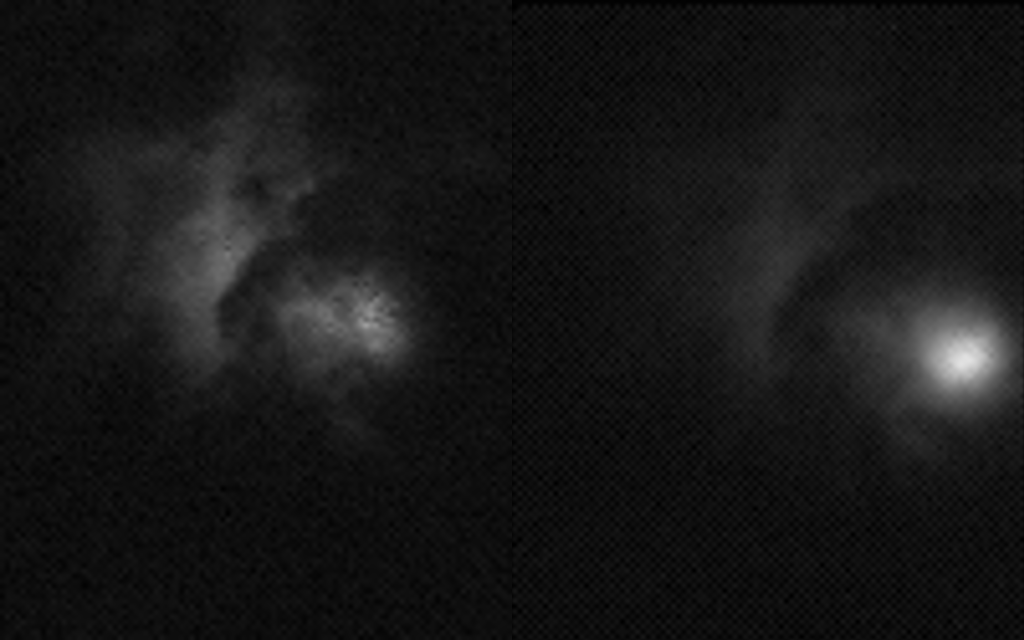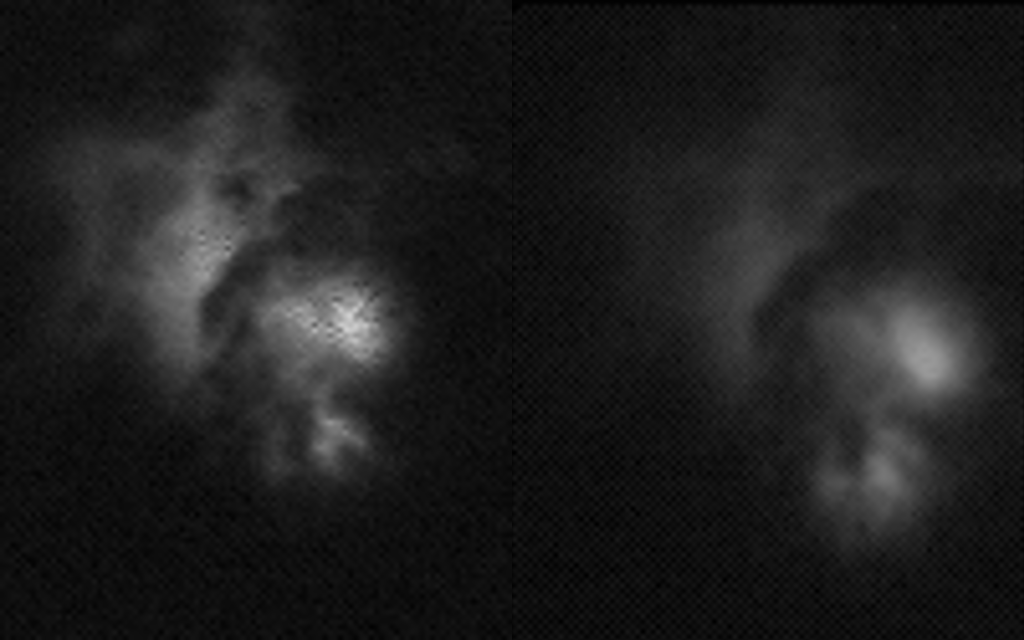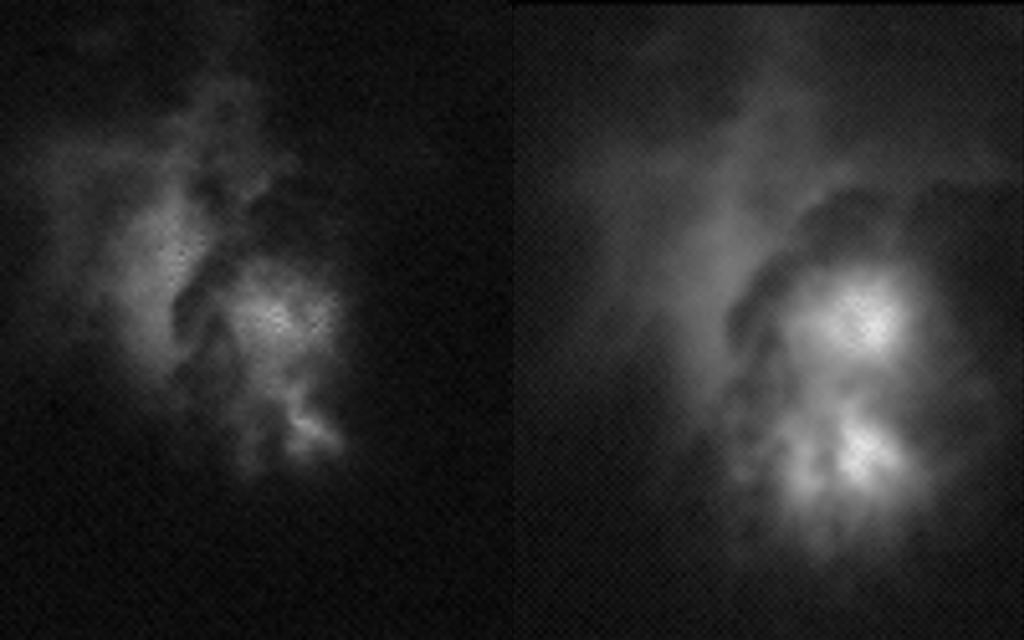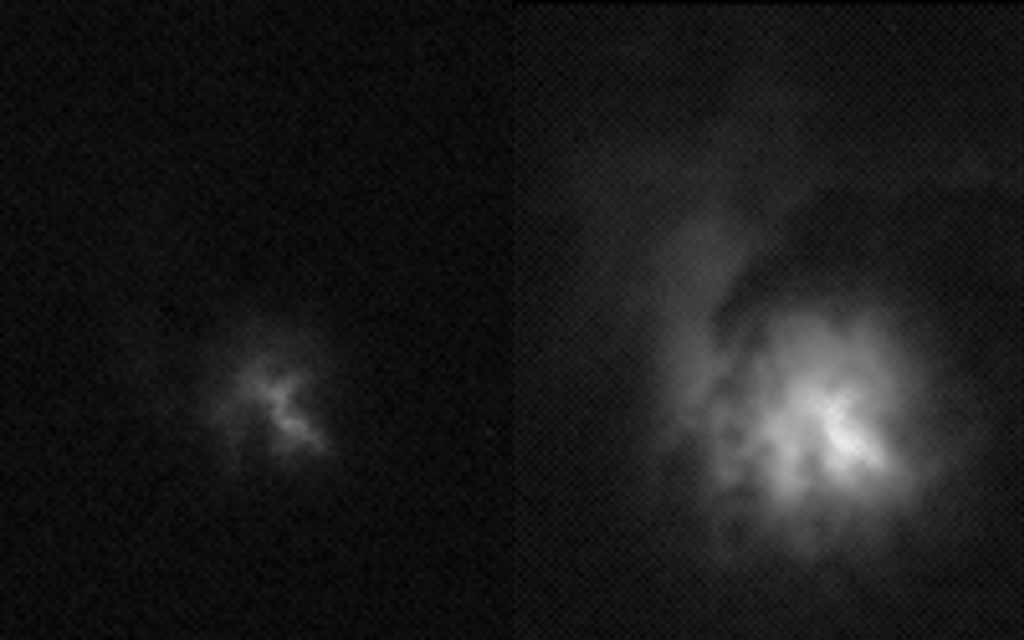
The first images and data captured the strong signature of lightning with unprecedented accuracy 400 kilometres above Earth.
“We collected 100 000 measurements per second of this amazing force of nature,” explains Torsten Neubert, science team coordinator at the Technical University of Denmark, “this is a fantastic example of how powerful our photometers are”.
Elves and the power of light

The observatory points straight down at Earth so the atmosphere filters as little of the light as possible. The storm hunter’s photometers are hundreds of times more sensitive than an average camera on Earth. In the storm above Indonesia the instruments recorded a spike across three wavelengths.
“Even with the clouds partly blocking the lightning, the instruments show powerful electrical discharges high in the atmosphere. We think it shows an elve,” says Torsten.
Elves are the highest of all the ‘transient luminous events’ known to date. In the blink of an eye concentric rings appear as a dim, expanding glow hundreds of kilometres wide formed by electrons colliding and excited nitrogen molecules.
The images are surprisingly similar to a sequence captured by ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen from the International Space Station in 2015.
“Thanks to Andreas’s discovery we know exactly how to interpret the images,” says Torsten. The data will allow scientists to investigate the phenomenon, and distinguish between layers of lightning and other high-energy discharges.
More to come
Setting up one of the most complex facilities ever flown on Columbus is a matter of trial and error. Each element is tested, including measures to avoid sunlight burning the sensors.
The first images are from the facility's visual cameras. A second suite of instruments detects high and low energy and has not finished calibration yet.
The first images are only a taster of its capabilities. “The most exciting science is yet to come – we will soon be able to correlate these optical data with terrestrial gamma-ray measurements,” ends Torsten.